Jump to a section
Business finance refers to the money and funding that your business needs to operate and grow. It's the lifeblood of your company - you simply can't run a successful business without proper financial management.
As a small business owner, finance is crucial because it allows you to purchase the things your business requires, cover your day-to-day costs, and invest in growth. In essence, business finance underpins every aspect of running your company. It's not just about having money - it's about managing that money strategically to achieve your goals and grow your small business.
In this guide, we'll explore the key components of business finance that every business owner should be familiar with. From navigating financial statements to exploring financing options, budgeting and forecasting techniques, and managing cash flow, we'll provide you with the tools and strategies to strengthen your financial management practices.
Key takeaways
- Know your financial statements - Things like your balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow report can show you the health of your business. Check them regularly.
- Plan your money - Make a budget to see where your cash is coming from and going. Also, try to forecast your future finances to spot potential issues.
- Find the right funding - There are different ways to get extra money, like loans or investors. Weigh the pros and cons to pick what works best for your business.
- Stay on top of it all - Keep close tabs on your cash flow, taxes, risks, and investments. This will help you make smart decisions to keep your business stable and growing.
Financial statements demystified
As a small business owner, understanding your company's financial statements is crucial for making informed decisions and assessing the overall health of your business. Let's take a closer look at the three essential financial statements you should be familiar with:
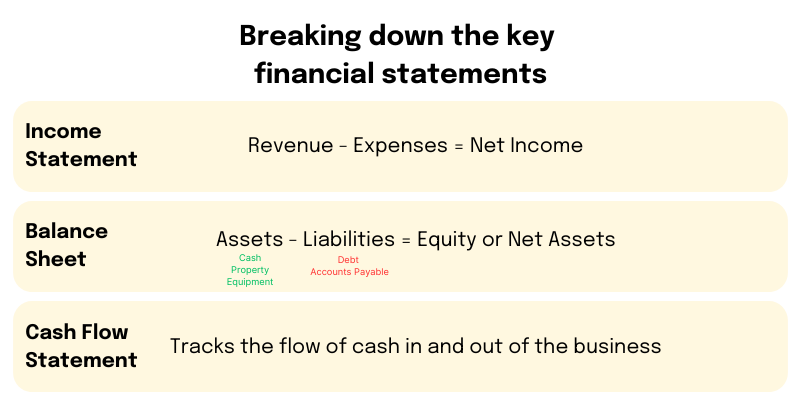
The balance sheet
The balance sheet is a snapshot of your business's assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. It shows what your business owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and the difference between the two (equity). This statement helps you understand the financial position of your business and whether you have enough resources to cover your obligations.
For example, let's say your balance sheet shows that you have £50,000 in cash and £20,000 in outstanding invoices (accounts receivable). This means you have £70,000 in current assets. On the liabilities side, you have £30,000 in outstanding bills (accounts payable) and a £20,000 loan. Your equity, which is the difference between your assets and liabilities, would be £20,000. This information can help you assess your company's ability to pay its bills and make informed decisions about investing in new equipment or expansion.
The income statement
Also known as the profit and loss statement, the income statement shows your business's revenue, expenses, and net profit (or loss) over a specific period, such as a month or a year. This statement is essential for understanding your business's profitability and identifying areas where you can improve your financial performance.
Imagine your income statement shows that you generated £200,000 in revenue last year, but your expenses were £180,000. This means your net profit was £20,000. By reviewing this statement, you can see where your business is making money and where you might need to cut costs or focus on more profitable areas of your operations.
The cash flow statement
The cash flow statement tracks the movement of cash in and out of your business. It shows how much cash you have on hand, how much cash you've generated from your operations, and how much cash you've used for investing and financing activities. This statement is crucial for understanding your business's liquidity and ensuring you have enough cash to meet your obligations.
Let's say your cash flow statement shows that you had £50,000 in cash at the beginning of the year, and you generated £80,000 in cash from your operations. However, you used £60,000 to purchase new equipment and paid off £20,000 in loans. This means you ended the year with £50,000 in cash, which can help you plan for future investments, expansions, or unexpected expenses.
Understanding the purpose of each of these is key to assessing the overall financial health of your small business. By regularly reviewing these statements, you can identify trends, spot potential issues, and make informed decisions to improve your business's financial performance.
Key components of business finance
Budgeting and forecasting
A budget is the foundation of sound financial planning. It helps you allocate your resources wisely, identify areas where you can cut costs, and ensure you have enough funds to cover your expenses. By creating a budget, you'll have a clear picture of your expected income and expenses, allowing you to make informed decisions about investing in new opportunities or saving for a rainy day.
Let’s take a look at a step-by-step guide on how to create one:
- Start by listing all your expected sources of income, such as sales, investments, or any other revenue streams.
- Next, itemise your fixed expenses, like rent, insurance, and loan payments, as well as your variable expenses, such as materials, utilities, and marketing costs.
- Compare your projected income to your expected expenses and identify any potential gaps or surpluses.
- Allocate your resources accordingly, prioritising essential expenses and finding ways to cut back on non-essential costs.
- Regularly review and update your budget as your business grows and circumstances change.
While budgeting helps you manage your current financial situation, forecasting allows you to predict your future financial performance. By using historical data, market trends, and industry insights, you can create educated projections about your revenue, expenses, and cash flow.
Some common forecasting techniques include:
- Sales forecasting: Predicting future sales based on past performance and market trends.
- Cash flow forecasting: Estimating the inflow and outflow of cash to ensure you have sufficient liquidity.
- Profit and loss forecasting: Projecting your expected revenue, expenses, and net profit.
Remember, budgeting and forecasting are not one-time exercises - they require ongoing attention and adjustment as your business evolves.
Cash flow management
Cash flow refers to the money you receive from sales, investments, and other sources, and the money you pay out for expenses, purchases, and other costs. Tracking your cash flow helps you see how much cash you have on hand at any given time.
Maintaining positive cash flow is essential for keeping your small business running smoothly. If you don't have enough cash to cover your bills and day-to-day costs, you could run into serious problems.
Here are some strategies to help you optimise your cash flow:
- Get paid faster: Send out invoices promptly and follow up with customers to ensure they pay on time. You could also offer discounts for early payment.
- Time your payments wisely: Negotiate good payment terms with your suppliers and pay your bills just before they're due, so you can hang onto your cash for longer.
- Manage your inventory: Avoid tying up too much money in stock that isn't selling quickly. Keep a close eye on your inventory levels.
If you're facing cash flow problems, don't worry - here are some of our top tips:
- Prioritise your essential expenses and talk to your suppliers or creditors if you need more time to pay.
- Look into financing options like business loans or invoice factoring to bridge any gaps.
- Review your pricing to make sure you're making a good profit.
- Find ways to cut costs, like renegotiating contracts or eliminating unnecessary spending.
- Use forecasting to predict and plan for any future cash flow issues.
By staying on top of your cash flow, you'll keep your small business running smoothly and be able to take advantage of new opportunities when they arise.
Financing Options for Small Businesses
It’s likely that at some point you’ll need access to additional funds as your company grows. Luckily, there are lots of options available to you! Let’s explore some of the most common ones and what you should consider when deciding which one is right for you and your business.
Financing sources for small businesses
- Business loans: Traditional bank loans or loans from alternative lenders can provide a lump sum of capital to invest in your business. These typically have fixed repayment terms.
- Lines of credit: A line of credit gives you access to a flexible, revolving source of funds that you can tap into as needed. This can be helpful for managing cash flow.
- Venture capital: Venture capitalists may invest in your business in exchange for equity or ownership. This can provide significant funding, but you'll have to give up a portion of your company.
- Crowdfunding: Platforms like Kickstarter or Indiegogo allow you to raise money from a large number of individual investors, often in exchange for a product or perk.
Each financing option has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, loans offer predictable repayment terms, but you'll need to qualify and provide collateral. Venture capital can provide a big injection of funds, but you'll have to share ownership and control of your business.
Pros and cons of financing options
When choosing a financing option, consider factors like:
- How much capital you need
- How quickly you need the funds
- The cost of the financing (interest rates, fees, etc.)
- How much control you're willing to give u
- Your ability to repay it
How to apply for a loan for your business
If you decide to pursue a business loan, be prepared to provide detailed financial information to lenders. This may include:
- Your business plan
- Financial statements (balance sheet, income statement, cash flow)
- Projections and forecasts
- Information about your industry and competition
- Details on how you'll use the loan funds
Presenting a strong, well-organised case will improve your chances of securing the financing you need.
Remember, it’s important to take the time to explore your options and choose the approach that best aligns with your business goals and financial situation.
Financial ratios and analysis
Financial ratios are an important tool for understanding the health and performance of your small business. These ratios take the information from your financial statements and turn it into meaningful insights that can guide your decision-making.
Profitability ratios
These ratios help you understand how profitable your business is. Some examples include:
- Profit margin: Shows the percentage of revenue that turns into profit.
- Return on assets: Measures how efficiently you're using your assets to generate profit.
- Return on equity: Indicates how much profit you're generating for your shareholders.
Liquidity ratios
Liquidity ratios assess your ability to meet your short-term financial obligations. Important ones include:
- Current ratio: Compares your current assets to your current liabilities.
- Quick ratio: Similar to the current ratio, but excludes inventory, which can be harder to convert to cash.
Leverage ratios
These ratios reveal how much your business relies on debt to finance its operations. Examples are:
- Debt-to-equity ratio: Compares your total debt to your total equity.
- Interest coverage ratio: Shows how easily you can pay your interest expenses.
Using this information, you can make more informed decisions about things like pricing, cost-cutting, investment, and more. Maybe you need to improve your margins or find ways to reduce your debt. Regularly reviewing your financial ratios will help you identify areas for improvement and put your small business on a stronger financial footing.
Tax planning and compliance
As you know, taxes are a big part of your financial obligations! But effective tax planning can save your small business a lot of money. By understanding your tax responsibilities and identifying legal ways to reduce what you owe, you'll have more resources to reinvest in your company's growth.
Tax planning can help you:
- Maximise deductions and take advantage of tax credits
- Determine the best business structure for tax purposes
- Plan for future tax obligations and avoid surprises
- Ensure you're in compliance with all relevant tax laws and regulations
Tax considerations for small businesses
As a small business owner, there are several tax-related factors to keep in mind, including:
- Deductions: You may be able to deduct business expenses like equipment, office supplies, utilities, and even a portion of your home if you use it for work.
- Credits: Depending on your industry and location, you could qualify for tax credits that directly reduce the amount of tax you owe.
- Compliance: Make sure you're filing all necessary tax forms, such as income tax returns, payroll taxes, and sales tax, on time and accurately.
Tax-saving strategies
To minimise your small business's tax burden, consider these strategies:
- Consult a tax professional: An accountant or tax advisor can help you identify legal ways to reduce your taxes and ensure you're in compliance.
- Time your income and expenses: Strategically time when you recognise income and claim deductions to manage your tax obligations.
- Take advantage of tax-advantaged accounts: Things like retirement plans and health savings accounts can provide tax benefits.
- Research available tax incentives: Look into government programmes, industry-specific tax credits, and other incentives that could apply to your business.
Risk management and insurance
Running a business means you’re always defending against various risks - from unexpected property damage to liability claims. Effective risk management and the right insurance can help safeguard your company.
Understanding business risks
Risks can come from many sources, both internal and external to your business. Some common examples include:
- Property damage or theft
- Injuries or accidents involving employees or customers
- Lawsuits and liability claims
- Disruptions to your operations, such as a natural disaster or technology failure
The importance of risk management
Proactively identifying and mitigating these risks is crucial for the health of your business. Risk management allows you to:
- Minimise the potential for costly incidents
- Keep your business open in the face of disruptions
- Protect your assets and reputation
- Comply with applicable laws and regulations
Insurance options for small businesses
One of the most effective ways to manage risk is by investing in appropriate insurance coverage. Some key policies to consider include:
- Property insurance: Protects your physical assets, such as your building, equipment, and inventory, in the event of damage or theft.
- Liability insurance: Covers claims of injury, property damage, or negligence that could be brought against your business.
- Business interruption insurance: Replaces lost income if your operations are temporarily suspended due to a covered event.
How to select the right coverage
When choosing insurance policies, consider the unique needs and risks associated with your small business. Factors to evaluate include:
- The value and nature of your physical assets
- The types of services or products you provide
- The number and roles of your employees
- Your location and potential exposure to natural disasters or other external threats
Don't forget to review your coverage regularly and adjust it as your business grows and evolves.
Investment and growth strategies
Investing in strategic initiatives can help fuel your growth, but it's important to carefully consider where you allocate your resources. Here are some key investment and growth strategies to keep in mind.
Investing for business expansion
When it comes to growing your small business, there are several areas you could choose to invest in, such as:
- Acquiring new equipment or technology to improve efficiency
- Expanding your product or service offerings to reach new markets
- Opening additional locations or branches to increase your geographic footprint
- Investing in marketing and advertising to boost your brand awareness and customer base
When evaluating these investment opportunities, think about the potential return. How will the investment directly contribute to increasing your sales, reducing your costs, or strengthening your competitive position? Make sure the benefits justify the upfront costs and risks involved.
Balancing short-term and long-term goals
It's important to find the balance between pursuing short-term financial gains and investing in the long-term health of your business. Short-term goals might be things like increasing your profitability this year or improving your cash flow. Longer-term objectives could be expanding into new product lines or breaking into a new market.
As you decide where to invest your resources, consider how each opportunity aligns with both your immediate and future goals. Look for ways to allocate funds that address current needs while also positioning your business for sustained success down the line.
For example, upgrading your equipment might have a quicker payoff in terms of improved efficiency and productivity. But investing in developing a new product could take more time and resources upfront, yet have a bigger impact on your long-term growth and competitiveness.
The bottom line
Effective financial management is essential for the success and growth of your small business. By applying the strategies covered in this guide, you can take control of your business finances and position your company for sustainable success.
Regularly review your financial statements, monitor cash flow, and stay on top of tax planning. Don't hesitate to seek advice from financial professionals as needed. With a strong understanding of business finance and a commitment to proactive management, you'll be well on your way to achieving your short-term and long-term goals.
Explore our blogs and guides if you need further support. Remember, sound financial practices will be the engine that drives your small business forward.
This does not constitute financial or tax advice. Please consult an accountant or financial advisor if you would like more information.











